
In this instance, you would go surfing but if we adjust the weights or the threshold, we can achieve different outcomes from the model. If we use the activation function from the beginning of this section, we can determine that the output of this node would be 1, since 6 is greater than 0. With all the various inputs, we can start to plug in values into the formula to get the desired output.

W3 = 4, since you have a fear of sharksįinally, we’ll also assume a threshold value of 3, which would translate to a bias value of –3.W2 = 2, since you’re used to the crowds.W1 = 5, since large swells don’t come around often.Larger weights signify that particular variables are of greater importance to the decision or outcome. Now, we need to assign some weights to determine importance. X3 = 1, since there hasn’t been a recent shark attack.Then, let’s assume the following, giving us the following inputs: Has there been a recent shark attack? (Yes: 0, No: 1).Let’s assume that there are three factors influencing your decision-making: The decision to go or not to go is our predicted outcome, or y-hat. We can apply this concept to a more tangible example, like whether you should go surfing (Yes: 1, No: 0). Let’s break down what one single node might look like using binary values. This process of passing data from one layer to the next layer defines this neural network as a feedforward network. This results in the output of one node becoming in the input of the next node. If that output exceeds a given threshold, it “fires” (or activates) the node, passing data to the next layer in the network. Afterward, the output is passed through an activation function, which determines the output. All inputs are then multiplied by their respective weights and then summed. These weights help determine the importance of any given variable, with larger ones contributing more significantly to the output compared to other inputs. Once an input layer is determined, weights are assigned. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and depression, are widely thought to be caused at least partially by brain dysfunctions, although the nature of such brain anomalies is not well understood.Output = f(x) = 1 if ∑w1x1 + b>= 0 0 if ∑w1x1 + b < 0
More common are genetically based diseases, such as Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and many others. Infection of the brain is rare because of the barriers that protect it, but is very serious when it occurs.

The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a wide variety of chemicals that can act as neurotoxins.

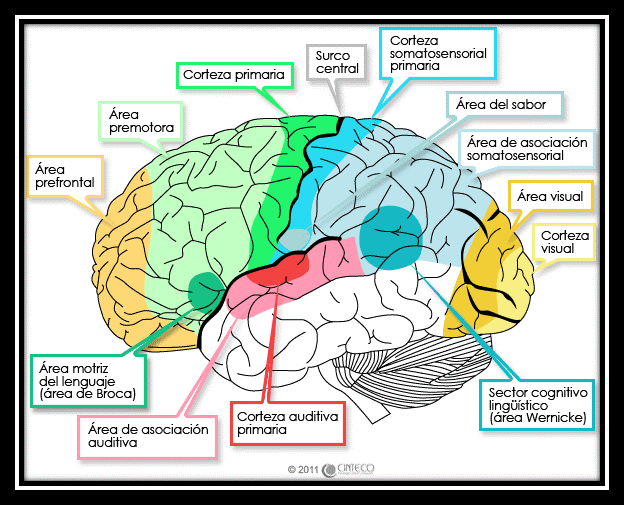
In spite of the fact that it is protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood-brain barrier, the delicate nature of the human brain makes it susceptible to many types of damage and disease. These cells pass signals to each other via approximately 100 trillion (1014) synaptic connections. The human brain has been estimated to contain 50–100 billion (1011) neurons, of which about 10 billion (1010) are cortical pyramidal cells. The portion of the brain devoted to vision is also greatly enlarged in humans.īrain evolution, from the earliest shrewlike mammals through primates to hominids, is marked by a steady increase in encephalization, or the ratio of brain to body size. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. Most of the expansion comes from the cerebral cortex, a convoluted layer of neural tissue that covers the surface of the forebrain. Enclosed in the cranium, it has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times as large as the brain of a mammal with an equivalent body size. The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
